- Additive manufacturing
- Advanced membranes
- American Physical Society
- ASC
- Astrophysics
- Atmospheric, Earth, and Energy
- Batteries
- Battery materials
- Bay Area Science Festival
- Biofuels sfa
- Biological Accelerator Mass Spectrometry
- Biosciences and Biotechnology
- Biosecurity
- Biosecurity & Bioscience
- Biosecurity and Bioforensics Group
- Biosecurity sfa
- Capacitive deionization
- Carbon nanotubes
- Carbonate materials
- Center for Accelerator Mass Spectrometry
- Center for Applied Scientific Computing
- Center for High Energy Density Science
- Charity
- Climate change
- Climate science
- Community
- Community gift program
- Computing & Simulation
- Counterterrorism
- COVID-19
- Ct vaccine center
- DARPA
- Data Science
- Data Science Institute
- Defense and Deterrence
- Discovery Center
- Diversity
- DOE
- Education
- Emergency
- Energetic Materials Center
- Energy flow charts
- EOS and Materials Theory Group
- Expanding Your Horizons
- Forensic Science Center
- Fun with science
- Fundamental Science
- Fusion
- Gemini Planet Imager
- Glenn T. Seaborg Institute
- HEAF
- High Energy Density Science
- HOME Campaign
- HPC
- HPC Innovation Center
- HPC4Mfg
- Hydrogen production
- Hydrogen storage
- IEEE
- Inertial confinement fusion
- Intelligence
- Internships
- Jupiter Laser Facility
- Laboratory for Energy Applications for the Future
- Laser Materials
- Lasers
- Lasers and Optical Science Technology
- Livermore Computing
- Livermore Valley Open Campus
- Livermorium
- LLMDA
- LLNS
- Machine learning
- Materials Science
- Microbiology and Immunology Group
- Nanocrystal solar cells
- Nanoscience
- NanoSIMS
- National Ignition Facility
- Neural devices
- Neutrinos
- Newsline
- nEXO
- NNSA
- Nonproliferation
- npneq
- Nuclear
- Nuclear and Chemical Sciences
- Nuclear and Particle Physics Group
- Nuclear Chemical and Isotopic Science
- Nuclear forensics
- NuSTAR
- Office of Science
- Outreach
- Oxidation and degradation
- pcmdi
- People
- Periodic table
- Physics
- Planetary Defense
- Postdocs
- Procurement
- Quantum Simulations Group
- Rare-earth elements
- Rubin Observatory
- Science
- Science and Technology Review
- Science on Saturday
- Sequestration
- Soil microbiome sfa
- Solar
- Solar system
- Solid-state batteries
- Space
- Space Science Institute
- STEM
- Stockpile stewardship
- Students
- Summer Student Spotlight
- Supercapacitors
- Supercomputer
- Supercomputing
- Surface analysis
- Sustainability
- Technology Transfer
- Tours
- Transport system
- Traumatic brain injury
- User Facility
- Veterans
- Viruses
- Water
- Water research
- Weapons
- Women in STEM
- Women's Hall of Fame
- WWW Research Landing Page
- X-ray
Back
Solar system
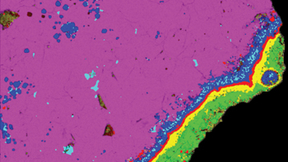
Meteorite made up of rare early solar system material
It looked like a fireball in the sky. It created a sonic boom. It vaporized upon entering the atmosphere. It's all of the above: The Sutter's Mill Meteorite had the force of 4 kilotons of TNT upon descent and spilled samples of itself over the towns of Columa and Lotus in northern California when it hit Earth last spring. And now a consortium of scientists including…
Putting the squeeze on planets outside our solar system
LIVERMORE, Calif. -- Just as graphite can transform into diamond under high pressure, liquid magmas may similarly undergo major transformations at the pressures and temperatures that exist deep inside Earth-like planets. Using high-powered lasers, scientists at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory and collaborators discovered that molten magnesium silicate undergoes a…
Oldest objects in solar system indicate a turbulent beginning
LIVERMORE, Calif. -- Scientists have found that calcium, aluminum-rich inclusions (CAIs), some of the oldest objects in the solar system, formed far away from our sun and then later fell back into the mid-plane of the solar system. The findings may lead to a greater understanding of how our solar system and possibly other solar systems formed and evolved. CAIs, roughly…
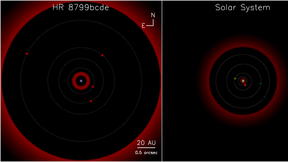
New pictures show fourth planet in giant version of our solar system
Astronomers have discovered a fourth giant planet, joining three others that, in 2008, were the subject of the first-ever pictures of a planetary system orbiting another star other than our sun. The solar system, discovered by a team from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory and the National Research Council of Canada (NRC) Herzberg Institute of Astrophysics with…