Back
Space Science Institute
"Mini" Device Set to Analyze Mysterious Psyche
As part of a NASA Discovery Program mission, an LLNL researcher is leading a team to develop an instrument for analyzing Psyche’s composition.
Space Program Innovation, One Small Satellite at a Time
Lawrence Livermore’s first involvement with CubeSats was developing optical imaging payloads for the Space-Based Telescopes for the Actionable Refinement of Ephemeris (STARE) project to monitor space debris. Since then, the Laboratory has continued to advance CubeSat technology and strengthen the institution’s space program.
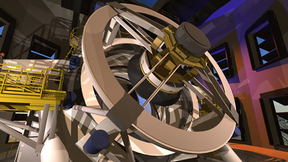
An Optical Revolution for X-Ray Imaging
Weighing nearly 4 kilograms, the first portable digital camera was built in 1975 and offered photographers the ability to capture black-and-white images with a resolution of .01 megapixels. Today, technological advancements have made it possible for people to carry much smaller, lighter, and significantly higher resolution cameras in their pockets (a standard smartphone…
New role for the Warm Electron Beam Ion Trap
In late October 2018, the Warm Electron Beam Ion Trap (WEBIT) was delivered to the NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC), where it is being used as a calibration source for the Resolve quantum microcalorimeter x-ray spectrometer. Resolve will be launched on the X-ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission (XRISM) in around 2022, and once in orbit, will measure x-ray emission…
Quest for source of black hole dark matter
Like a game of "hide and seek," Lawrence Livermore astrophysicists know that there are black holes hiding in the Milky Way, just not where. If they find them toward the galactic bulge (a tightly packed group of stars) and the Magellanic Clouds, then black holes as massive as 10,000 times the mass of the sun might make up dark matter. If they are only toward the galactic…
NIF and the Rise of LLNL’s Nanosatellites
To demonstrate a new paradigm in satellite construction and operation, LLNL researchers have been developing new instruments and operational principles for a type of nanosatellite called CubeSats.
Night or day, Lab-developed space-based telescope can image Earth and beyond
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers have developed and tested an optical telescope system that can be used for Earth and space observation. The team, led by Wim de Vries, built and tested several designs for high-resolution monolithic optical telescope systems, fabricated from a single piece of fused silica, for deployment on small satellites. After…
Unlocking the History of the Solar System
Detailed chronologic investigations performed by Livermore researchers using newly developed techniques to precisely date individual samples with confidence indicated that all the samples solidified within a narrow window of time.
The Widest, Deepest Images of a Dynamic Universe
Unaided and under the darkest conditions, the human eye can see only about 9,000 stars around Earth. The Large Synoptic Survey Telescope (LSST)—looking at only half of the night sky—is expected to detect an estimated 17 billion stars and discover so much more over the course of a 10-year mission.
Lab instrument will explore asteroid Psyche
In a few years, an instrument designed and built by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers will be flying hundreds of millions of miles through space to explore a rare, largely metal asteroid. The Livermore gamma ray spectrometer will be built in collaboration with researchers from the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory for the first-ever visit to…
CASTing new limits on the dark matter search
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers, along with international collaborators, are on a mission to find particles contributing to dark matter, which is expected to make up most of the matter in the universe. In a paper published May 2 in Nature Physics, the CERN Axion Solar Telescope (CAST) at CERN presented new results on the properties of axions --…
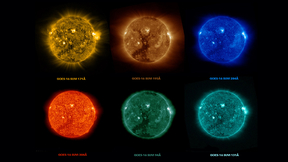
Here comes the sun in first-time images
The first images from the Solar Ultraviolet Imager (SUVI) instrument aboard the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s GOES-16 satellite capture a large coronal hole on the sun. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites (GOES) are part of NOAA’s space weather monitoring fleet. GOES-16 launched late last year. GOES-16 (known as "GOES-R" before its…
Astronomers discover cosmic double whammy
Astronomers have discovered a cosmic one-two punch unlike any ever seen before. Two of the most powerful phenomena in the universe, a supermassive black hole and the collision of giant galaxy clusters, have combined to create a stupendous cosmic particle accelerator.By combining data from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory, the Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (GMRT) in India…
Lab technology on board space weather monitoring satellite
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists and collaborators have developed a key technology for one of the instruments that are flying on board the next generation of Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites (GOES), as part of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)’s space weather monitoring fleet launched late last month.GOES-R…
Making an Impact on Asteroid Deflection
When it comes to asteroids—rare but potentially cataclysmic threats to global security—the best defense is a good offense. The most hazardous planetary objects are near-Earth asteroids (NEAs), those found to be in orbits that allow them to enter Earth's neighborhood.
Here is what it will take to avoid extinction by asteroid
Sixty-five million years ago, a catastrophic impact forever changed the environmental landscape of Earth – and there was no way to see it coming. This Earth-bound asteroid – or maybe several – changed the course of millions of years of evolution, altered the composition of our atmosphere – and the geology of Central America for good measure.
Lab plays role in striking view of Mercury transit
Around 13 times per century, Mercury passes between Earth and the sun in a rare astronomical event known as a planetary transit. The 2016 Mercury transit occurred on May 9 between roughly 4:12 a.m. and 11:42 p.m. PDT.NASA's stunning video of the transit of Mercury across the sun was made possible in part by work done by Lawrence Livermore scientists. Regina Soufli, a…
These space rocks could save the planet
The box was inconspicuous, but Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) postdoctoral researcher Megan Bruck Syal immediately knew its contents: two meteorites around the size of walnuts. They formed about 4.6 billion years ago and survived a history of violent collisions in the asteroid belt before being bumped into a near-Earth-object orbit by gravitational…
New research explores asteroid deflection using spacecraft to crash into body at high speeds
Asteroids headed for a collision with the Earth, if found early enough, can be acted upon to prevent the potentially devastating consequences of an impact. One technique to divert an asteroid, called kinetic impact, uses a spacecraft to crash into the body at high speeds.This approach delivers the momentum of the spacecraft, while also providing an additional boost of…
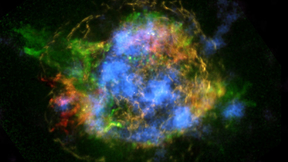
An X-Ray Eye on Universes
Answers to many scientific mysteries lie in realms invisible to the human eye. Clues to some of the most fundamental questions in astronomy, cosmology, and nuclear science lurk in sections of the electromagnetic spectrum outside the small slice of wavelengths one can see.